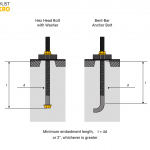
Although it may appear trivial, anchor bolt spacing is important when making installations. Using the right spacing ensures the proper mounting of structures, vessels, and equipment. In this article, we discuss more about anchor bolt spacing, how to determine it, applicable codes, and considerations when using sill plates.
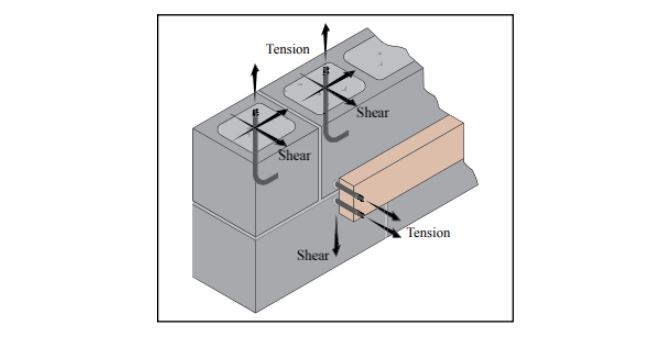
More About Anchor Bolt Spacing
The basic function of anchor bolts is to transfer loads from an attachment to concrete. Due to design forces such as uplift, anchors undergo tension and shear. As a result, anchors exert outward pressure on the surrounding wall in the concrete hole. This pressure has its epicenter at the base of the anchor, radiating up and outwards to the concrete surface with a cone-shaped appearance as the figure below highlights.
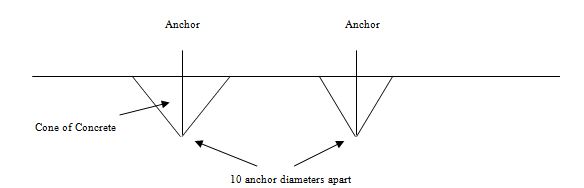
The concrete area within this cone experiences the pressure and represents the holding values of the anchor bolt. If two anchors are close such that their cones overlap, there will be a reduction in their holding strength. Thus, the need for sufficient anchor bolt spacing.
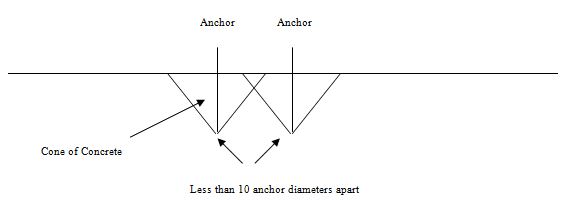
How To Determine Anchor Bolt Spacing
In practice, anchor bolt spacing on any project is carried out on the basis of industry or company guidelines. However, the defining factor in spacing is to avoid interference with the concrete cones of anchors. As highlighted earlier, these cones or pressure regions in the concrete are a function of either tension or shear.
Critical Spacing for Tension
When the anchor bolt is in tension, there is a possibility of failure due to concrete breakout. The area of concrete under the risk of breakout coincides with the concrete cone. Generally, the assumption is that breakout occurs at a prism angle of 35° to the horizontal axis as the figure below shows.
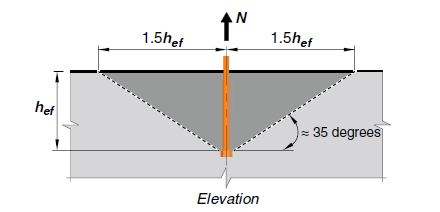
Denoting the effective embedment of the anchor bolt as (hef) leads to the critical spacing due to tensile force (N) being 3hef. Thus, the embedment of an anchor bolt is key to the spacing requirement. The deeper the embedment, the greater the spacing requirement to ensure a safe design.
Critical Spacing for Shear
When experiencing shear, the assumption of a 35° concrete cone angle remains the same as shown below in the plan view of the anchor.
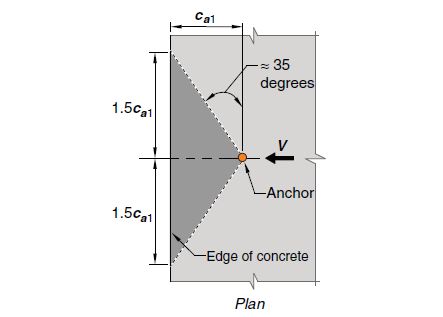
However, the parameter used to determine the critical spacing requirement is the distance from the center of an anchor shaft to the edge of concrete (ca1) in the direction of the shear force (V). Using these parameters, the critical spacing for an anchor bolt experiencing shear is 3ca1.
Applicable Codes
Although the previous section shows how to determine the critical spacing of anchor bolts, various design codes have their recommended values. The following sections preview sections of some applicable codes.
ACI 318
The ACI (American Concrete Institute) 318 contains recommendations for anchor bolt design and their installation in concrete. Some of these are as follows:
- The minimum center-to-center spacing of an anchor bolt shall be four times its diameter for cast-in anchors. For torqued anchors, it shall be six times its diameter.
- The ACI adopts ASCE’s recommendations for a minimum edge distance of four times the anchor bolt diameter for normal steel. Whereas anchors with high strength could use six times their diameter as a minimum allowance from the concrete edge.
IBC
The IBC (International Building Code) is another standard that encapsulates several specifications for an anchor bolt, including spacing recommendations. Other areas covered in this code include how to set anchor bolts in existing concrete or wet concrete, how long concrete should cure before bolt installation, the use of sill plates, and penetration requirements for bolts. Some of the details in the code are as follows:
- Anchor bolts shall be set in concrete after a curing period of between 3 to 7 days. Because at this point its design strength should be at least 60%.
- Penetration of bolts in concrete shall be a minimum of 7 inches (178 mm). In addition, the minimum allowable diameter of the bolt is ½ inch, but in seismic regions shall be 5/8 inches.
- If a building is two stories or less, the maximum anchor bolt spacing is 6 feet (152 mm). While buildings higher than two stories should have a maximum spacing of 4 feet (101 mm).
Considerations When Mounting Anchor Bolt To Sill Plate
Sill plates are horizontal members that are installed together with anchor bolts in some applications. They serve as base plates for the anchor and are often made from metal or wood. When in use, there are specifications to follow according to design codes such as the International Building Code (IBC).

- The maximum spacing of wooden sill plates should not exceed 6 feet if they are directly on concrete foundations. If the building in question is over two stories in height, then the maximum allowable spacing should decrease to 4 feet.
- On each sill plate, the IBC recommends the use of two anchor bolts. Also, each anchor bolt should be within the middle third of the plate width and have a spacing ranging between 4 inches and 12 inches from each end of the plate. Moreover, in seismic regions, it is advisable to increase the number of bolts per plate and reduce the spacing.
- For anchor bolts used on sill plates, the minimum permissible diameter is ½ inch. In addition, the minimum embedment of the bolt into the concrete is 7 inches. There are also size requirements for the washers used with the bolts, especially in regions prone to seismic loads. In such areas, the washer thickness should be at least 0.229 inches, with its length and width being 3 inches by 3 inches.