The double check valve, a backflow prevention device, safeguards against flow reversal. Such flow reversal can cause pump cavitation, contamination, or simply result in the suboptimal operation of a process system.
In this article, learn the function of a double check valve, installation, maintenance, repair, applications, and the differences between a double check valve and a backflow preventer.

Function
The double check valve only allows process media to flow through in one direction, preventing the backflow of contaminants.
Double-check valves consist of two non-return valves connected in a series, operating under two principles:
- Redundancy: If one check valve jams wide open, the other will still function.
- Pressure Differential: Closing one valve lowers the pressure differential across the other, thus resulting in a more trustworthy seal and preventing leakage.
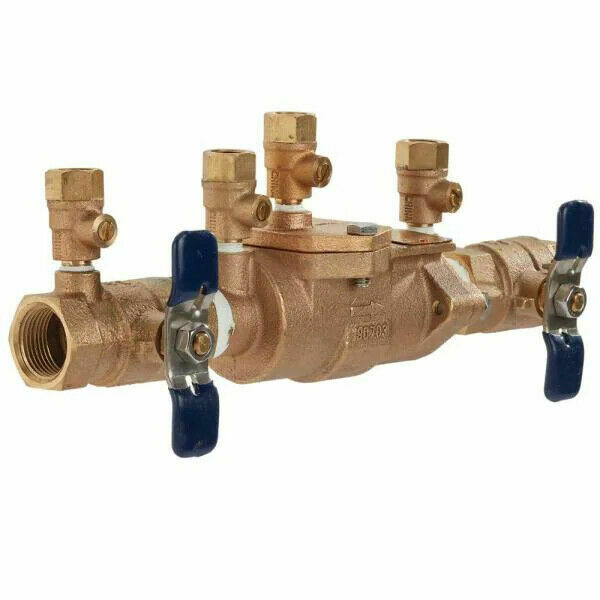

Installation
Double Check Valve Assembly
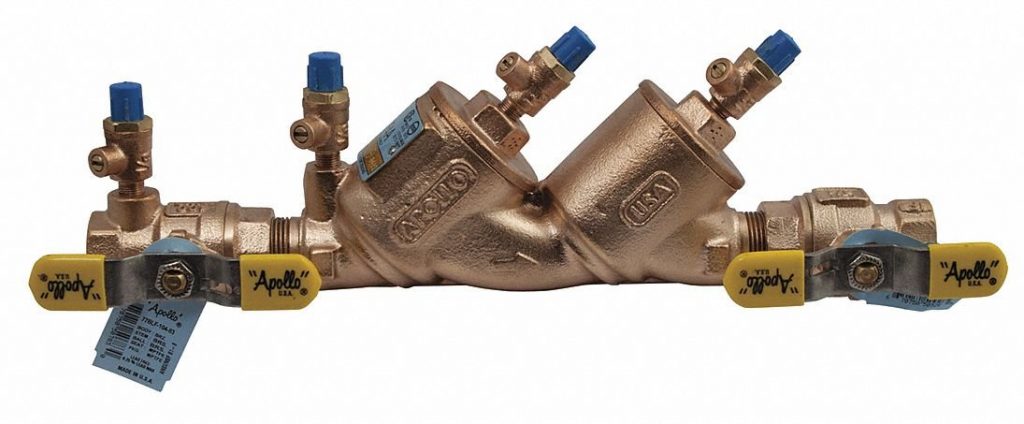

An engineer may specficy a double check valve as a pre-built assembly or specify each individual component. A pre-specified double check valve assembly (DCVA) provides a good voice for underground or interior space installations. It consists of an intake shutoff valve, two certified spring-loaded check valves, four test cocks, and an output shutoff valve.
Each check valve in the series may be spring-loaded inline, spring-loaded Y, a ball configuration, lift check, swing check, and stop check. The proper selection of the check valve type depends on economics, process media composition, and pressure and temperature conditions.
DCVA see installations either above ground or inline, horizontally or vertically, or where the potential for back-siphonage or backpressure is present.
Installation Requirements
Installation requirements depending on the piping specification and connection type. Some DCVA assemblies thread directly into fittings or associated piping. For large line sizes that see high pressure, flanged connections may be more appropriate.
Typically, technicians install assemblies in the horizontal position to reduce the possibility of cavitation.
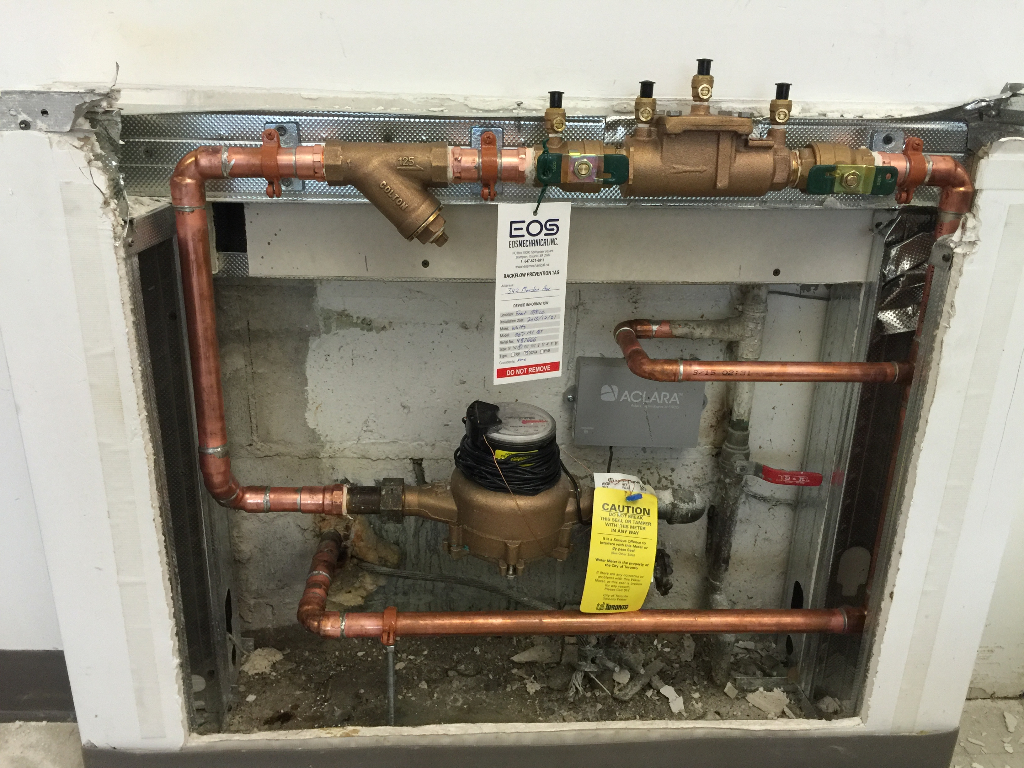

Maintenance
Double-check valves do not require routine replacement of components. However, to ensure the system operates properly, replace upstream filters according to manufacturers’ recommendations. Additionally, monitor pressure and pressure drops to ensure safe operation.
As part of the annual winterization and maintenance of the underground irrigation system valves, operators may open all valves on the assembly and clean out any debris from the valve box. Routine visual inspections ensure the system stays in proper operating condition.
Here are some of the tips:
- Have the assembly examined and tested according to local regulations.
- For installations that see intermittent use (think sprinkler systems), schedule inspections before the system reactivates in the spring to ensure a smooth start to the season.
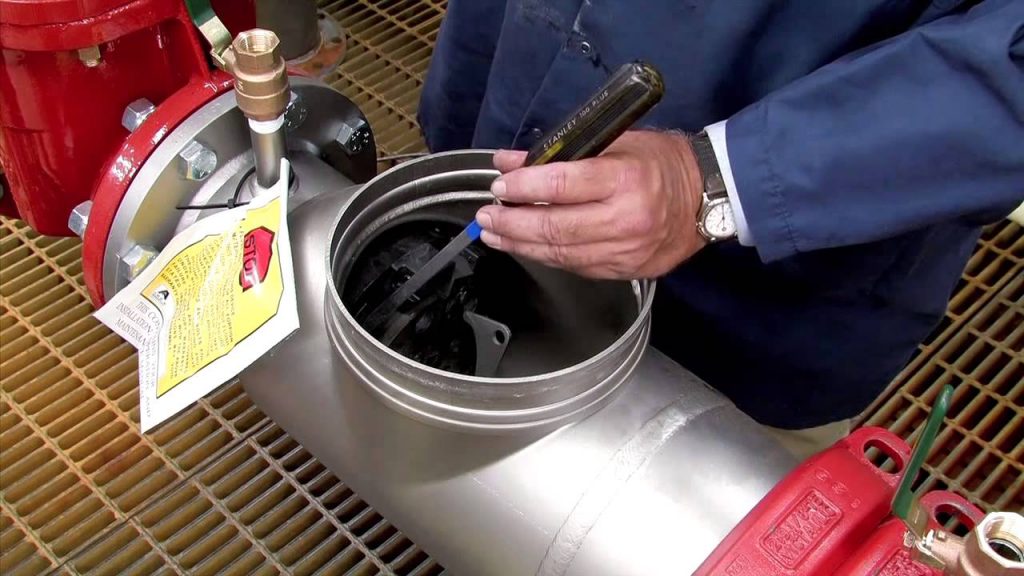

Repair
It’s straightforward to replace the entire double-check valve assembly with a new one. Remove the unions from the assembly portion and replace it with a new double-check valve assembly, pipe, and fittings. Then reconnect, check for leaks, and reintroduce flow.
However, it should be noted that several jurisdictions across the country have recently prohibited the use of double check valve assemblies or particular installation designs. Any “grandfather” protection is likely lost after the entire original assembly is taken out of service. It may need to be replaced with a new pressure vacuum breaker or lower pressure assembly if double check valve assemblies have been locally prescribed since it was installed. Before ordering a replacement double check valve assembly, check with your local authorities.
Double Check Valve Application
Backpressure and back-siphonage prevention is possible with the double check valve assembly, but not for high-hazard applications. A more reliable check valve, such as a lower pressure zone device, may be required if the hazard is higher, even if it is a relatively low hazard, such as putting antifreeze in the fire sprinkler system.

Air brake systems on heavy trucks, lawn irrigation, fire sprinkler, and combi-boiler systems usually use this material.
Double Check Valve vs. Double-Check Backflow Preventer
Backflow preventers and check valves look identical and appear to do the same thing, but there are a few crucial distinctions.
If you’re installing a valve on a water supply, backflow preventers generally provide a better option than a check valve. Because of backflow preventer fail-safe design, they are less likely to fail and contaminate a water supply. The cost tends to be more, but the additional safety measures that double-check backflow preventers provide makes it well worth it.

For installing a one-way valve on a sump pump line or other non-potable water lines, a check valve is a good option. Check valves are less expensive than backflow preventers, but they have a somewhat greater failure rate due to the failure of moving parts and seals.
Backflow Preventers and Check Valves differ primarily in their application. A backflow preventer is used in high-risk scenarios and is designed to fully protect potable water with its fail-safe design. In contrast, a check valve is used in low-risk situations and stops backward flow but lacks fail-safe components.
The savvy operator weighs the cost and benefits of each type of valve protection when designing a solution.