Single-phase and three-phase configurations are currently the most common AC power supply systems in use. Because each system has advantages over the other in certain applications, it is necessary to clearly highlight these features. In this article, we review both types of power supply systems, and compare the single-phase vs three-phase systems across various parameters.
Single-phase Power
In a single-phase configuration, only two wires serve for power supply. One is the phase or live wire that supplies current to the load in the setup, while the neutral is used to return this current to the source. Usually, the single-phase voltage is 230V, but in the US, residential supply has two live wires carrying 110V/115V each. So, equipment with low power demand use just one of the live wires, whereas those with higher power demands, such as washing machines, use both live wires. It is common to refer to this type of single-phase system as split-phase. Notably, both live wires in this system are in phase, with voltage rising and falling simultaneously. Thus, single-phase systems do not deliver constant power supply.
Advantages
- Single-phase power uses either one or two conductors to supply power to load, thereby offering a simple and economic design.
- It is ideal for power supply to domestic appliances such as fans, lights, and televisions. Even appliances such as heaters and air conditioners can utilize single-phase, especially in a split-phase setup.
- Depending on the application, it is used to supply loads of up to 2,500 Watts. Thus, offering a low power system that operates optimally and transmits efficiently.
Disadvantages
- Cannot meet starting torque requirements for low-power motors. Therefore, requires additional equipment to provide starting torque.
- This system is unable to meet power requirements of industrial motors and other heavy equipment.
- Also, the system has a poor power factor, which necessitates the installation of a capacitor.
Three-phase Power
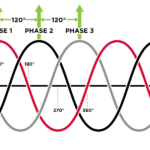
A three-phase connection delivers power using three conductors with each containing the same magnitude of power. Although, the power signal in each line is out of phase by 120°, a combination of the three phases ensures constant power delivery at every moment. Also, there is a balance in the power. As a result, a three-phase configuration may not have a neutral, depending on if it is a star or delta circuit.
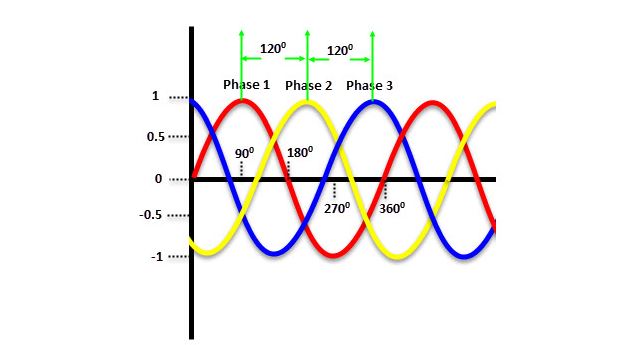
The figure above shows the variation in the power signals of a typical three-phase lines. During one 360° cycle, each phase peaks twice. So, power never drops to zero in the system. Rather, it remains generally stable. In addition, with three conductors/phases in the system, a significant amount of power is transferred, which makes it ideal for industrial systems.
Advantages of Three-phase
- An efficient way to power large loads for industrial and commercial purposes. Even residential electricity supply is three-phase in some regions.
- Unlike single-phase, three-phase can power large motors effectively without extra equipment to supply starting torque.
- Provides stable power that is balanced, if working perfectly. So, there is no need for a neutral wire in some settings.
Disadvantages of Three-phase
- Because of the large amount of power that the wires transmit, there is need for significant amount of insulation.
- Three-phase connections are susceptible to damage from overload. In addition, three-phase components are expensive vs single-phase.
Differences Between Single-phase and Three-phase
Single-phase and three-phase are both AC power systems, but there are several differences between them as the following table highlights.
| Singe-phase | Three-phase |
| Flow of electricity is via a single conductor. But in a split-phase configuration, the same phase passes through two separate conductors. | Electricity flow is through three conductors, with each one transmitting a different phase. |
| Because of it is only one phase, there is variation in power supply, which is not suitable for some applications. | The combination of the three phases ensures constant power levels. |
| If there is any issue with the phase line, there will be power outage. | Offers redundancy, as other lines can function if there is a failure in one line. |
| Capable of delivering up to 230 Volts. | While three-phase can carry up to 415 Volts. |
| Needs extra circuitry to generate rotational magnetic field. | Generates rotational magnetic field without extra circuitry. So, it is ideal for large motors. |
| Power losses are high, so it is good for distribution over short distances. | Relatively lower power losses make it ideal for long-distance transmission. |
| The use of neutral wire is necessary to return current from the load. | No neutral wire in a delta connection, while it is optional for a wye/star connection. |