Manhole benching refers to the concrete haunching that lies between the walls of a manhole and the channel pipes passing through. Moreover, benching plays a vital role in improving the hydraulic performance across a manhole and helps with maintenance in the long term. In this article, we review the purpose of manhole benching, its construction process, and the manhole rehabilitation process.
Purpose of Manhole Benching
Benching in manholes creates a well-defined path for wastewater to flow in a certain direction, thereby eliminating the splashing of waste. This is important especially where there are incoming branch lines because splashing can cause waste build-up in the manhole, thus, leading to blockages. For this reason, the installation of benching requires a minimum pitch that ensures the return of any waste overspill into the channel pipe. Also, the finishing of the surface is smooth to make it self-cleaning and minimize resistance to flow.
Due to the tight-fitting of the concrete around the channel pipes and its smooth and near-vertical finish, ensures it is difficult for rodents to escape from the system. Thus, there should be no gaps between the benching and the channel pipes. Another function of benching is that it serves as the platform for maintenance personnel to stand when carrying out their operations.
Manhole Benching Process
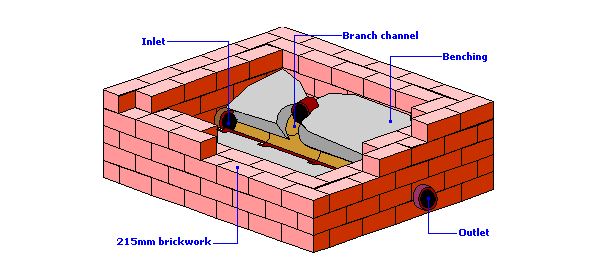
The manhole benching process is one of the key finishing touches in the construction of a manhole. It comes after excavation, making a concrete bed, and setting up the brick masonry for the manhole. Manhole benching involves concrete haunching using the right mix to define the channels. A basic requirement is a smooth and neat finish as the figure below shows.

The depth of the benching is a function of the drain size and the channel depth at the center above the concrete bed. Below is a table highlighting the relationship of these three parameters.
| Size of Drain (cm) | Channel Depth (cm) | Benching Depth (cm) |
| 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 15 | 20 | 30 |
| 20 | 25 | 35 |
| 25 | 30 | 40 |
| 30 | 35 | 45 |
| 35 | 40 | 50 |
| 40 | 45 | 55 |
| 45 | 50 | 60 |
Benching Mix Ratio
An important aspect of manhole benching is selecting the appropriate concrete mix for the application. A sand and cement mix is sufficient for most domestic manholes, while bigger sites use a sand, cement, and grano mix to give a superior finish. So, for domestic needs, a 1:3 sharp sand mortar mix would do, then the granolithic mortar should be 1 part sand, 2 parts cement, and 6 parts grano. Also, the gradient for the screed should lie between 1:10 to 1:30.
Benching Design Considerations
When constructing a manhole benching, key things to consider are:
- Hydraulic performance: Sewer designs have a minimum velocity requirement to ensure self-cleaning. The hole benching strategy must be such that it reaches this self-cleaning velocity at least once a day. Else, waste will drop out of the water flow, leading to blockages.
- Scoring: Although minimum velocity is important for self-cleaning, there needs to be a maximum velocity in the system. This is because solid particles move at high velocities and could produce an abrasive effect on concrete and internal pipe walls.
- Solid content: Sewer systems that are prone to having large solid particles within should adopt half-benching, which gives room for waste evacuation. Relatively clean and debris-free networks can use full benching.
Manhole Rehabilitation Process
Over time, the need to repair, restore, or upgrade a manhole system will arise. Because manholes provide access for any kind of repair on sewer networks, the level of degradation should not be extreme before intervention. As a result, regular inspection of its components is necessary to give a clear picture of the extent of damage per time.
Rehabilitation of the manhole components could involve any of several techniques including grouting, cementing, paneling, and mechanical repairs. One of the manhole components susceptible to failure is the benching, because of its regular contact with wastewater. Erosion of the benching is a common failure mode, and usually occurs in areas where the benching meets the channel pipes. When this happens, there is water loss to the subsoil undermining the chamber, which could cause tree root ingress and even movement.
Isolation of the manhole from inflow is necessary before carrying out repairs. This helps prevent water from touching the concrete before setting. After isolating the manhole from inflow, the damaged section of the benching is removed and recasted. If the damage is excessive, it is advisable to completely remove the benching and make a new one. This helps to ensure continuity and smoothness of the surface. Also, it provides the opportunity to correct any defects in the initial design. In any case, it will be necessary to use chemical additives that will expedite the curing process, to avoid shutting down the system for long.
Common Manhole Rehabilitation Solutions
Some of the common manhole rehabilitation solutions in the industry are as follows:
- Cementitious liners: This is an easy-to-use low-cost lining for repairing manholes. Usually, their application is during a low-pressure spraying process, but using them is not advisable in a corrosive environment due to infiltration.
- Manhole grouting with chemical injections: This involves applying gel within the manhole to seal and waterproof cracks and prevent inflow. It is an advisable option for manhole structures subject to leaking such as benching but is not ideal for those that are failing. A more advanced approach is needed when the deterioration of structures is at an advanced level.
- Cured-in-place manhole liner: This solution uses a felt tube that contains resin in its core to tightly secure the manhole because inflating the tube hardens the resin. Generally, it requires more equipment and larger crews than other trenchless rehabilitation methods but is ideal for cylindrical manholes.
- Geopolymer manhole linings: These are cement-based linings that coat the manhole, thereby forming a seal to support the structure. Unlike cementitious liners, they are good for corrosive environments and provide structural enhancement.



