During the construction of various structures, there are different methods of interfacing pipe flanges, fittings, and other connecting parts. Out of these methods, using a butt weld or socket weld is popular. In this article, you will learn about butt weld construction vs socket weld construction, and compare the differences between the two.
Butt Weld Construction
Unlike a socket weld, a butt weld involves placing two metal workpieces together and welding along the joint. This welding should be done in a way that the heat penetrates the faying surfaces of the two workpieces as much as possible. Thus, making the joints from this process more robust than from other types of welding. To ensure proper butt weld construction, there are certain requirements to follow:
- The two workpieces that make up the joint should be of the same diameter or thickness, depending on their geometry. Also, they should be put together end to end.
- If the two parts coming together are thin plates, then there is no surface preparation requirement. The basic cleaning of the edges will suffice. However, as the edges get thicker, making bevels on the faying surfaces becomes necessary to improve weld penetration.
- Proper alignment is key to forming a solid butt joint and tack welding helps to achieve this. Subsequently, multiple weld passes strengthen the joint.
- Butt welds could be partial or full penetration, depending on the strength requirements and access to both sides of the joints. When both sides of the joint can be accessed, full penetration is preferable because it provides higher strength. Back-gouging is a necessary step to take during full penetration welding to avoid distortion effects and ensure weld root integrity. If only one side is accessible, then using a back-strip and a thicker weld root is often sufficient.
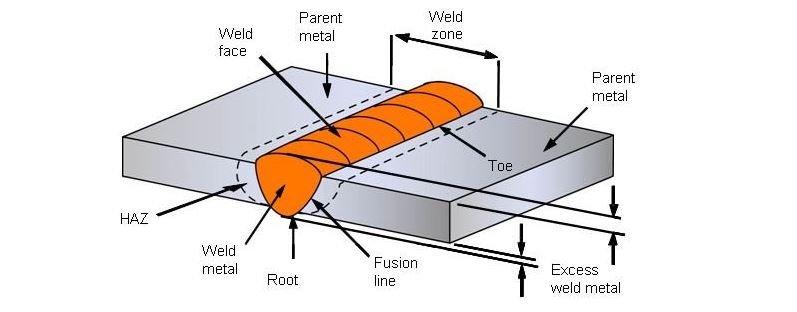
Advantages of Butt Weld
There are several merits in using a butt weld for an application vs other types of welds, such as a socket weld. Some of them are as follows:
- Butt welds offer significant joint penetration, and in some cases, they are CJP welds. Moreover, this gives them a much stronger connection, making them ideal for high pressure applications.
- Also, the high strength joints they offer makes them suitable for large diameter pipelines and thick sheet metals.
- The robustness of butt welds means they are good for use on a wide variety of metals.
Disadvantages of Butt Weld
Although butt welds are robust, there are downsides of using them in certain applications.
- One reason to discourage the use of butt welds is the requirement of extensive surface prep. As the parent material gets thicker, there is need for more intensive preparation. As a result, the process is more expensive and complex than most methods.
- In addition, performing a good butt weld requires higher level of welding skills. Further adding to the cost of the process.
Socket Weld Construction
Unlike a butt weld that puts together similar workpieces, a socket weld is used for joining sections with significant size difference. Ideally, this is the welding method for joining pipes with varying cross-section, or for fitting a pipe into a valve. Making up these joints involves the use of square-cut fittings or flanges to aid alignment and embedment of parts. Then, a fillet weld around the edges of the bigger workpiece seals the joint. These features make it a popular choice for making joints when there is a change in direction in a piping network.

Advantages
- The most attractive feature of a socket weld is that it is effective in joining sections of different sizes and materials.
- Although a socket weld requires fittings, which are expensive, they do not require robust surface preparation like a butt weld.
- It requires only fillet welds which are easy to implement, so there is no demand for high welder skill level.
Disadvantages
- Because fillet welds have low weld penetration, the strength and stress resistance is lower than in butt welds. As a result, socket welds are not ideal for very high-pressure systems.
- Also, socket welds are not suitable for systems containing fluids that are sensitive to contamination or reaction with the welding.
Differences Between Butt Weld and Socket Weld
This section compares the features of a butt weld vs a socket weld across different parameters.
| Parameter | Butt Weld | Socket Weld |
| Strength | A typical butt weld has excellent durability, good temperature resistance, and deals with corrosion better than a socket weld. | Reliable choice for welding pipes that transmit steam up to 600 PSI. Also available for high-pressure rating classes 3,000, 6,000, and 9,000. |
| Size or thickness of parent material | Generally, for joining workpieces of the same size. Also, its superior strength makes it suitable for large diameter pipes. | Ideal for connecting pipes and workpieces that have different sizes. Because of the strength of its joint, it is used for pipe diameter range of DN50 to DN100. |
| Surface preparation | Requires significant surface preparation including beveling ends from 30° to 37.5°. | Only cleaning of the faying surfaces is necessary. |
| Non-destructive testing | A butt weld has more complex weld testing requirements than a socket weld. However, can be 100% tested using only x-ray. | Magnetic particle testing is used for carbon steel, while penetrant testing is ideal for stainless steel. |
| Cost | More expensive to design, test, install, and maintain. Also requires welding at a higher skill level. | Simplicity of design, lack of surface preparation, and less complicated testing makes it cheaper. |
| Industry standard | ASME B16.9 is key in the construction of butt welds. | Socket weld pipe fittings are defined by ASME B16.11. |



